

Andhra Pradesh, located in southeastern India, is known for its rich history, cultural heritage, and agricultural abundance. With Amaravati as its capital and Visakhapatnam as the largest city, Andhra Pradesh is famously called the "Rice Bowl of India" due to its extensive rice production. The state is home to magnificent temples, beautiful beaches, and vibrant festivals that showcase its unique identity. From the sacred Tirupati Temple to the picturesque Araku Valley, Andhra Pradesh presents a perfect blend of spirituality, nature, and tradition.

Andhra Pradesh stands unique in Indian history as a region with a rich legacy of ancient kingdoms and empires. The area was ruled by powerful dynasties like the Satavahanas, Ikshvakus, Pallavas, Chalukyas, Kakatiyas, and Vijayanagara Empire, creating a distinct cultural identity that sets it apart from other Indian states.
The Satavahana dynasty (2nd century BCE - 2nd century CE) established one of the first great empires in South India, with their capital at Amaravati. They were great patrons of Buddhism and Hinduism, and their rule saw the development of distinctive art and architecture, particularly the magnificent Amaravati Stupa. The Satavahanas played a crucial role in maritime trade with the Roman Empire.
The Ikshvaku dynasty succeeded the Satavahanas and continued the tradition of religious patronage. The Pallavas and Chalukyas later vied for control of the region, each contributing to the architectural and cultural landscape. The Kakatiya dynasty (12th-14th centuries) built impressive fortifications like the Warangal Fort and established a strong administrative system.
The Vijayanagara Empire (14th-17th centuries) marked a golden age for the region, with magnificent temple architecture and flourishing arts and literature. The empire's capital at Hampi was one of the largest cities in the world at its peak. After the fall of Vijayanagara, the region came under the Qutb Shahi dynasty and later the Nizams of Hyderabad.
Andhra Pradesh's modern history began with the formation of Andhra State in 1953, the first linguistic state in India. This was merged with the Telugu-speaking areas of Hyderabad State to form Andhra Pradesh on November 1, 1956, under the States Reorganization Act. The state was bifurcated in 2014, creating the new state of Telangana.
Today, Andhra Pradesh takes pride in this unique heritage. The temples of Tirupati, Srisailam, and Simhachalam, along with the Buddhist sites at Amaravati and Nagarjunakonda, attract visitors from around the world. The state's vibrant culture, characterized by its classical Kuchipudi dance, Carnatic music, and rich literary tradition, reflects this blended historical legacy.
Andhra Pradesh's ancient legacy is not just historical; it's a living tradition that continues to shape the state's identity. From the architecture of its temples to the rhythm of its music and the flavors of its food, this heritage makes Andhra Pradesh a fascinating example of cultural continuity and resilience.
Andhra Pradesh is known for its rich cultural heritage, which is reflected in its linguistic diversity. The state's language landscape showcases its unique history as the heartland of Telugu culture and literature.
Telugu is the official language of Andhra Pradesh and is spoken by the majority of the population. It belongs to the Dravidian language family and has a rich literary tradition dating back over a thousand years. Telugu is known as the "Italian of the East" due to its melodic quality and is one of the six classical languages of India.
The languages of Andhra Pradesh reflect its unique position as the cultural heartland of Telugu civilization. While Telugu remains the soul of Andhra identity, the presence of Urdu, tribal languages, English, and Hindi creates a rich linguistic tapestry that mirrors the state's history as a meeting point of different cultures.
Andhra Pradesh's festivals reflect its deep spiritual traditions and agricultural heritage, creating a cultural calendar that is vibrant, colorful, and deeply rooted in tradition. From grand temple celebrations to harvest festivals, Andhra Pradesh festivals showcase the state's devotional spirit and cultural diversity.
Sankranti is the most important and widely celebrated festival in Andhra Pradesh, known for its vibrant celebrations, traditional rituals, and community feasts. This harvest festival marks the transition of the sun into the zodiac sign of Capricorn and is celebrated with great enthusiasm across the state.

The Sankranti festival is more than just a harvest celebration; it is a manifestation of Andhra Pradesh's agricultural soul that transcends religious and cultural boundaries. With its vibrant rituals, traditional foods, and community spirit, Sankranti perfectly embodies Andhra's unique identity as a land where nature and culture coexist harmoniously.
Ugadi is the Telugu New Year festival celebrated with great enthusiasm across Andhra Pradesh. This festival marks the beginning of a new year according to the lunisolar calendar and is characterized by special prayers, traditional rituals, and festive foods.
Ugadi, which means "the beginning of a new age," is calculated based on the lunar cycle and typically falls in March or April. The festival begins with ritual oil baths, wearing new clothes, and visiting temples. Families prepare special dishes and gather to celebrate the new beginning with hope and optimism.
Ugadi is a testament to Andhra Pradesh's rich cultural traditions and its celebration of time and renewal. The rituals and festivities displayed during this festival reflect the philosophical depth of Telugu culture and its connection to cosmic cycles and human experiences.
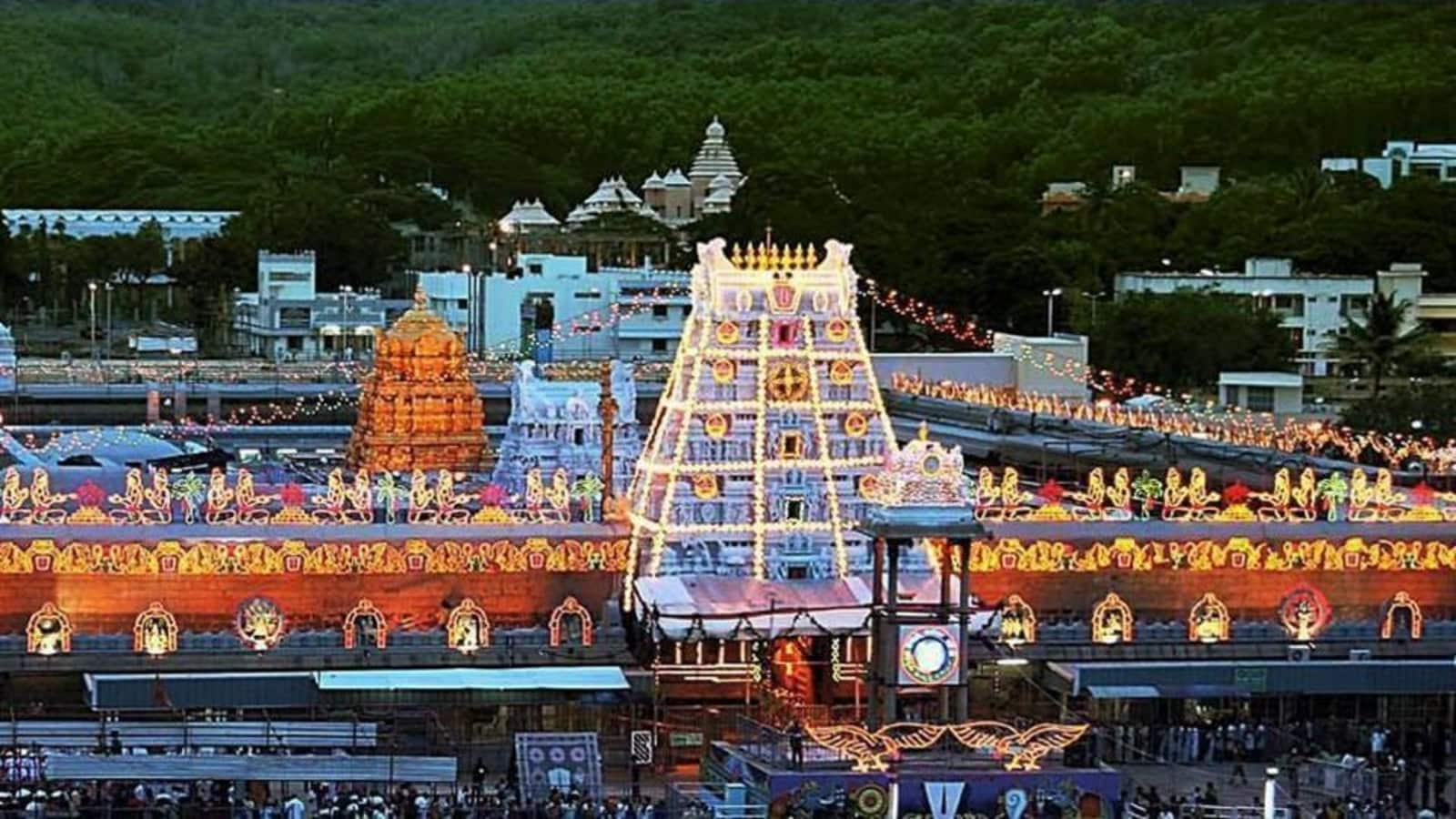
Brahmotsavam at Tirumala is one of the most important religious events in Andhra Pradesh, attracting millions of devotees from around the world. This nine-day festival at the Tirumala Venkateswara Temple is celebrated with grand processions, religious rituals, and cultural performances.
Brahmotsavam represents the rich religious heritage of Andhra Pradesh, showcasing traditional rituals and devotional practices. As a festival that has been celebrated for centuries, it connects modern Andhrites to their spiritual roots while adapting to contemporary times.
The festivals of Andhra Pradesh showcase its unique cultural synthesis, where Hindu, Muslim, and Christian traditions coexist and often influence each other. This harmonious blend of celebrations reflects the spirit of Andhra Pradesh - devotional, inclusive, and deeply rooted in both agricultural and spiritual traditions.
Andhra Pradesh, known as the "Koh-i-Noor of India," is a state of rich cultural heritage, historical significance, and natural beauty. From ancient temple towns to modern port cities, each urban center in Andhra Pradesh has its own distinct character, contributing to the state's reputation as a land of spirituality, agriculture, and emerging development.
Visakhapatnam, often called Vizag, is the largest city in Andhra Pradesh and known as the "Jewel of the East Coast." Located on the Bay of Bengal, it serves as the economic capital of the state and is a major port city, industrial hub, and tourist destination. Vizag beautifully balances its natural beauty with industrial development.



RK Beach (Ramakrishna Beach) is the heart of Visakhapatnam's tourism, known for its beautiful shoreline, parks, and entertainment options. The beach is named after the Ramakrishna Mission located nearby and stretches along the Bay of Bengal, offering stunning views of the sunrise and sunset.

The beachfront is developed with well-maintained parks, including the Taraka Rama Park and the VUDA Park, which feature musical fountains, children's play areas, and food stalls. The Kursura Submarine Museum, located on the beach, is a unique attraction where a real submarine has been converted into a museum showcasing naval history.
RK Beach is not just a tourist attraction but also a popular recreational spot for locals. Morning walkers, joggers, and yoga enthusiasts frequent the beach, while evenings see families and couples enjoying the sea breeze. The beach also hosts various cultural events and festivals throughout the year.
Today, RK Beach represents Visakhapatnam's identity as a coastal city that values both development and quality of life. Its combination of natural beauty and urban amenities makes it a must-visit destination in Andhra Pradesh, showcasing the state's connection to the sea and its modern aspirations.

The Simhachalam Temple is one of the most important Hindu temples in Andhra Pradesh, dedicated to Lord Narasimha, an incarnation of Vishnu. Located on the Simhachalam Hill about 16 km from Visakhapatnam, the temple is known for its unique architecture and spiritual significance.
The temple complex features exquisite Kalinga architecture with intricate carvings and sculptures. The main deity is usually covered with sandalwood paste, which is removed only once a year during the Chandanotsavam festival. The temple's history dates back to the 11th century, with contributions from various dynasties including the Eastern Ganga dynasty and the Gajapati kings.
Simhachalam Temple is not only a place of worship but also an architectural marvel. The temple's main tower (gopuram) rises to a height of about 50 feet, featuring detailed carvings of various deities and mythological scenes. The temple premises include several mandapams (halls), water tanks, and gardens that add to its spiritual ambiance.
Today, the Simhachalam Temple attracts thousands of devotees and tourists throughout the year. The temple represents Andhra Pradesh's rich religious heritage and architectural traditions. Its hilltop location offers panoramic views of Visakhapatnam and the surrounding countryside, making it both a spiritual and visual delight for visitors.
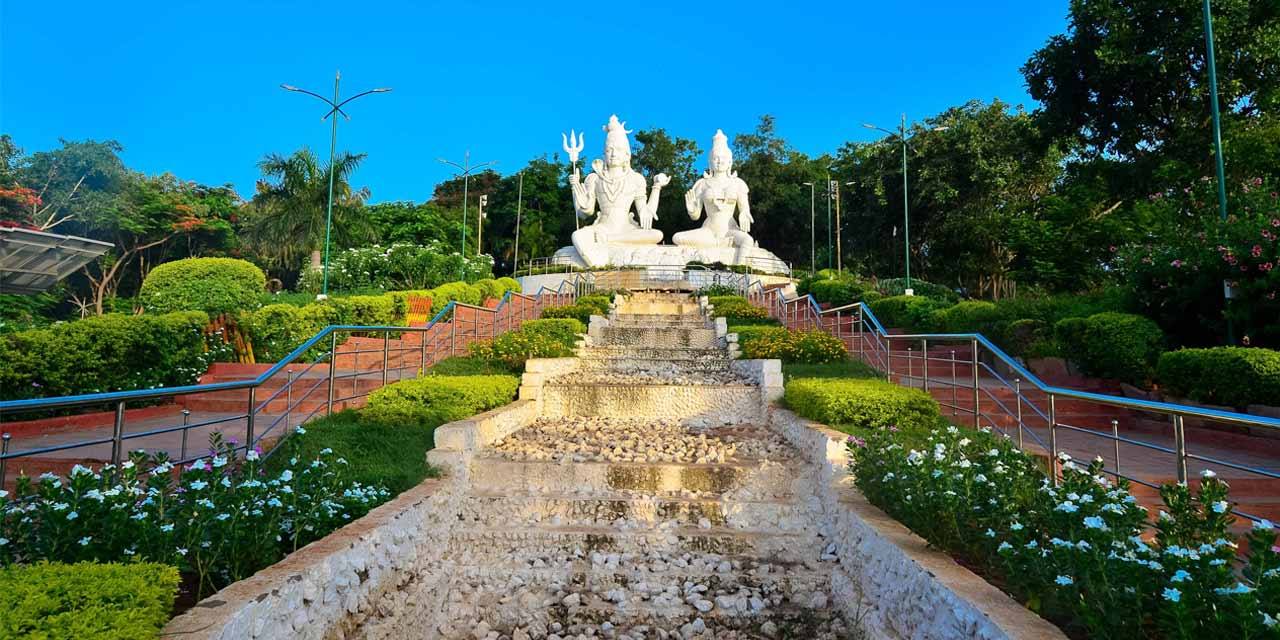

Kailasagiri is a beautiful hilltop park in Visakhapatnam that offers breathtaking views of the city, the Bay of Bengal, and the surrounding hills. Developed and maintained by the Visakhapatnam Urban Development Authority (VUDA), Kailasagiri has become one of the most popular tourist destinations in Andhra Pradesh.
The park spans over 100 acres and features beautifully landscaped gardens, sculptures, and recreational facilities. The main attractions include the 40-foot tall statues of Shiva and Parvati, the Floral Clock, and the Shanku Chakra Nama decorations on the hill slopes. A ropeway connects the hilltop to the beach road, providing visitors with a thrilling ride and spectacular views.
Kailasagiri is not just a viewpoint but a comprehensive entertainment destination. It features toy train rides for children, well-maintained walking tracks, and various viewpoints strategically placed to offer different perspectives of the city and sea. The park is particularly popular during sunrise and sunset when the views are most spectacular.
In recent years, Kailasagiri has undergone significant development with the addition of new attractions and improved facilities. The park represents Visakhapatnam's commitment to creating quality urban spaces that enhance residents' quality of life while attracting tourists. It stands as a testament to the city's ability to balance natural beauty with recreational development.
Araku Valley is a stunning hill station located about 115 km from Visakhapatnam in the Eastern Ghats. Known for its coffee plantations, waterfalls, and tribal culture, Araku Valley offers a perfect escape from the coastal heat and urban bustle. The valley is situated at an altitude of about 3,200 feet above sea level.
The journey to Araku Valley is as spectacular as the destination itself, with the Kirandul passenger train passing through numerous tunnels and bridges, offering breathtaking views of the hills and valleys. The valley is home to several tribal communities, particularly the Bagata, Gadaba, Jatapu, and Valmiki tribes, who have preserved their traditional way of life.
Key attractions in Araku Valley include the Borra Caves, which feature fascinating stalactite and stalagmite formations; the Katiki Waterfalls, known for their pristine beauty; and the Coffee Museum, which showcases the history and process of coffee cultivation. The valley is also famous for its organic coffee plantations that produce some of India's finest coffee.
Araku Valley represents the natural diversity of Andhra Pradesh, showcasing a different aspect of the state beyond its coastal plains. The valley's cool climate, lush greenery, and tribal heritage make it a unique destination that complements Andhra's temple towns and beach cities. It demonstrates the state's geographical variety and its potential for diverse tourism experiences.
Visakhapatnam embodies the modern aspirations of Andhra Pradesh while respecting its natural heritage. As the largest city and economic capital, it offers industrial opportunities, natural beauty, and urban amenities while maintaining a unique character. From its beautiful beaches to its growing industries, Visakhapatnam is a city that captures the dynamic spirit of contemporary Andhra Pradesh.
Vijayawada, located on the banks of the Krishna River, is known as the commercial capital of Andhra Pradesh. The city serves as a major business, educational, and transportation hub and is centrally located in the state. Vijayawada is famous for its ancient temples, vibrant markets, and cultural significance.
Vijayawada offers a glimpse into the commercial heart of Andhra Pradesh, balancing business activity with cultural heritage. As the commercial capital, it showcases the state's economic potential through its markets, educational institutions, and growing infrastructure. For visitors seeking to understand Andhra's business landscape, Vijayawada provides valuable insights into the state's commercial vitality.
Tirupati, located in the Chittoor district, is known as the spiritual capital of Andhra Pradesh and one of the most important pilgrimage centers in India. The city is famous for the Tirumala Venkateswara Temple, which attracts millions of devotees annually, making it one of the world's most visited religious sites.
Tirupati represents the spiritual soul of Andhra Pradesh, where devotion and tradition create a unique urban experience. As the spiritual capital, it showcases the state's deep religious roots through its temples, rituals, and pilgrimage culture. For visitors seeking spiritual enrichment, Tirupati offers a profound experience of Andhra's devotional heritage.
Guntur, located in the heart of Andhra Pradesh, is known as the agricultural hub of the state. The city is famous for its chili production and is a major center for agriculture, education, and commerce. Guntur serves as the administrative headquarters of Guntur district and plays a crucial role in the state's agricultural economy.
Guntur represents the agricultural backbone of Andhra Pradesh, where traditional farming practices thrive alongside modern agricultural techniques. The city's vibrant markets, especially the chili market, offer an authentic experience of Andhra's rural economy. For those seeking to understand the agricultural heritage of the state, Guntur provides valuable perspectives on Andhra Pradesh's role as the "Rice Bowl of India."
Kurnool, located in the Rayalaseema region of Andhra Pradesh, is known for its historical significance and natural attractions. The city served as the capital of Andhra State from 1953 to 1956 and has a rich history dating back to ancient times. Kurnool is famous for its historical sites, caves, and the Nagarjuna Sagar Dam.
Kurnool represents the historical depth of Andhra Pradesh, balancing ancient heritage with contemporary life. As a city with significant historical and archaeological importance, it showcases the state's rich past through its forts, caves, and cultural traditions. The combination of historical sites, natural attractions, and cultural heritage makes Kurnool an important destination for understanding Andhra Pradesh's diverse legacy.
The cities of Andhra Pradesh each contribute uniquely to the state's character. Visakhapatnam represents the industrial and coastal beauty, Vijayawada the commercial vitality, Tirupati the spiritual heritage, Guntur the agricultural strength, and Kurnool the historical depth. Together, these urban centers showcase the diversity that makes Andhra Pradesh much more than just a state—they reveal a region with ancient history, vibrant culture, and multiple economic strengths that balance tradition with progress. From magnificent temples to bustling commercial centers, from agricultural markets to industrial hubs, Andhra Pradesh's cities offer experiences that capture the essence of this dynamic Indian state.
Andhra Pradesh food is renowned for its fiery heat, bold flavors, and diverse vegetarian and non-vegetarian specialties. The cuisine reflects the state's agricultural abundance, coastal resources, and cultural diversity. Known as one of the spiciest culinary traditions in India, Andhra food offers a delightful experience for those who appreciate intense flavors.
Andhra Meals is the quintessential dining experience in the state, featuring a complete platter of various dishes served on a banana leaf. This traditional meal showcases the diversity and complexity of Andhra cuisine in a single sitting.
Andhra Meals is more than just a meal; it's a cultural experience that embodies the essence of Andhra hospitality and culinary tradition. Its complex arrangement and diverse flavors have evolved over centuries, making it the crown jewel of Andhra dining culture.
Gongura Pachadi is a signature Andhra dish that exemplifies the state's love for bold, tangy flavors. This chutney made from sorrel leaves is a staple in Andhra households and is known for its unique sour taste and vibrant red color.
Gongura Pachadi is a perfect example of Andhra's culinary creativity, where a simple leafy vegetable is transformed into a flavor-packed dish. Its unique taste and preparation tell the story of Andhra's agricultural roots and its ability to create distinctive food from locally available ingredients.
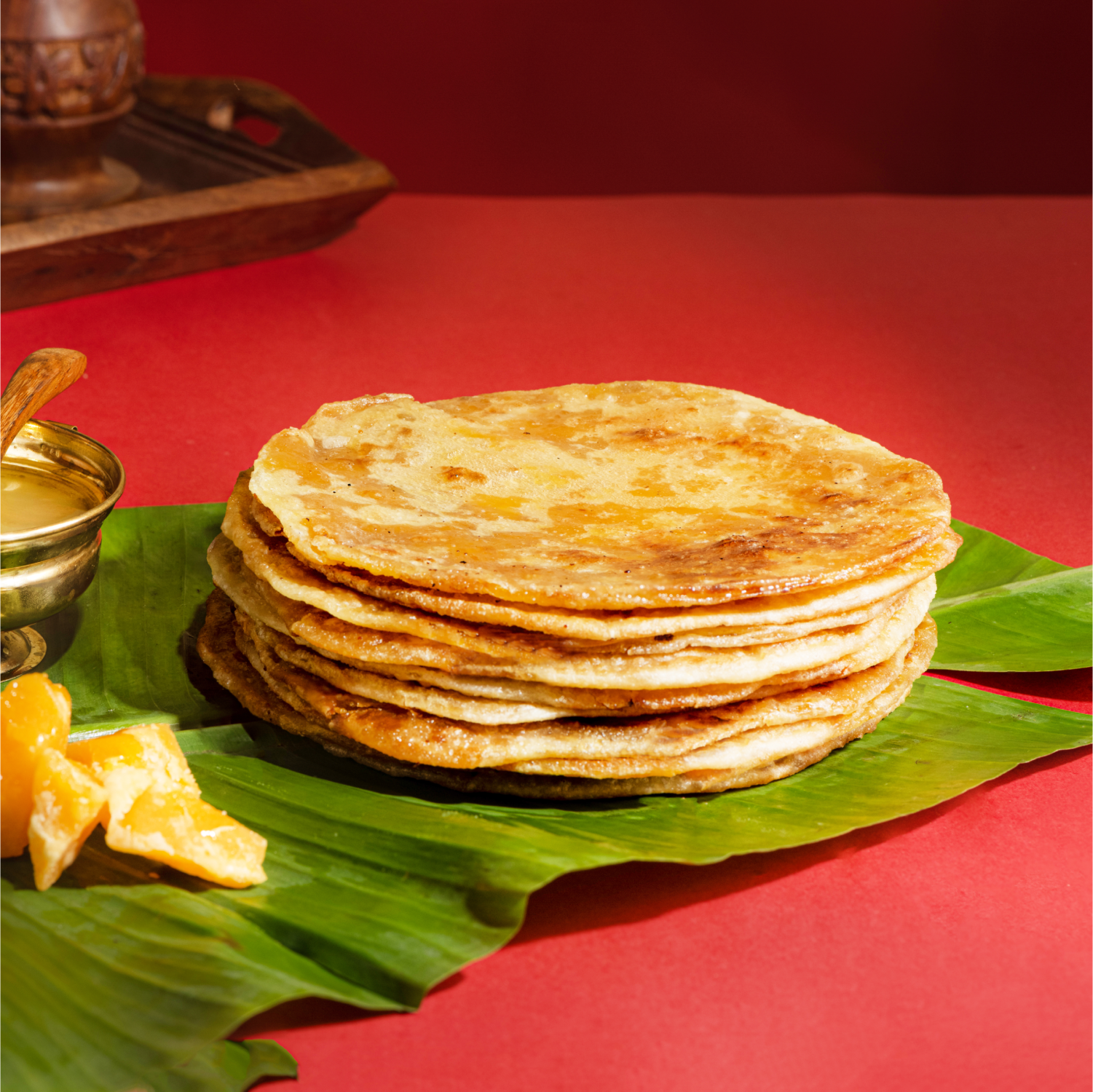
Pootharekulu is a traditional Andhra sweet that is as delicate in appearance as it is delicious in taste. This paper-thin sweet from the East Godavari district represents the sweet side of Andhra cuisine and is a staple at festive occasions.
Pootharekulu is more than just a sweet; it's a work of edible art that embodies the festive spirit of Andhra Pradesh. Each delicate layer represents the care and tradition that goes into Andhra cooking, making it a fitting conclusion to any Andhra meal and a sweet representation of the state's cultural heritage.
A fiery chicken curry known for its intense spice and rich flavor.

A tangy and spicy fish curry popular in coastal Andhra.

A nutritious soup made from horse gram, a specialty of Rayalaseema.
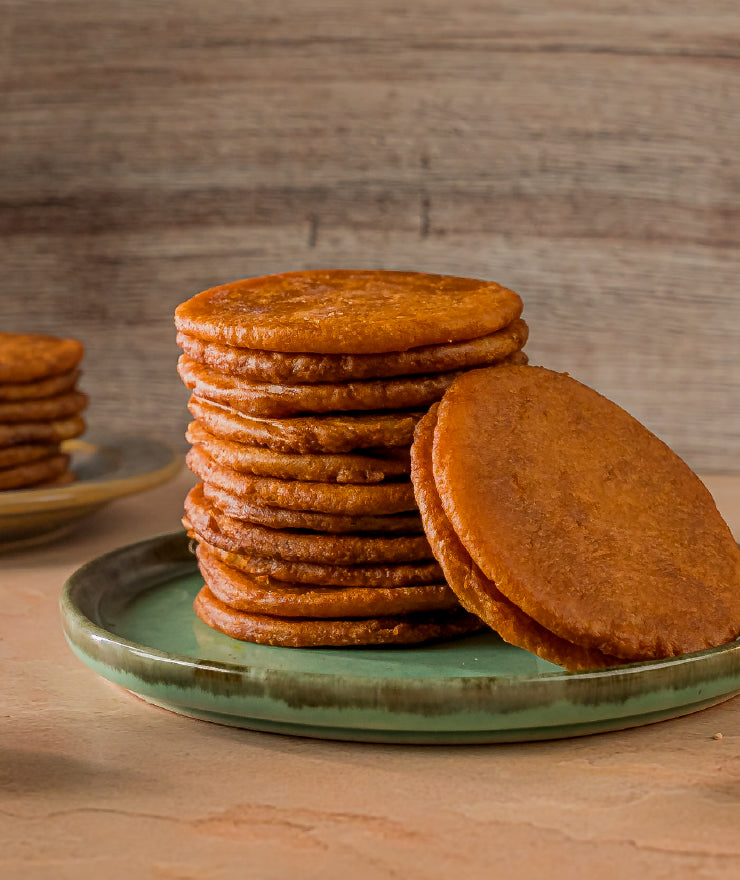

A traditional sweet made during Sankranti, featuring rice flour and jaggery.
Andhra Pradesh cuisine is a vibrant tapestry woven from indigenous Telugu traditions and regional variations, with additional touches from historical influences that have interacted with the region over centuries. From the fiery heat of Andhra meals to the delicate sweetness of Pootharekulu, Andhra food tells the story of a people who have mastered the art of balancing intense flavors. Each dish is not just nourishment but a celebration of Andhra's unique cultural identity and its position as a land of agricultural abundance and culinary excellence.
Andhra Pradesh fashion is a vibrant reflection of its agricultural heritage, temple traditions, and rich cultural diversity. From traditional attire that tells stories of rural life to contemporary styles influenced by urban centers, Andhra clothing represents a unique blend of comfort, elegance, and cultural identity. The fashion scene in Andhra Pradesh beautifully balances tradition with modernity, creating a distinctive style that is both functional and aesthetically pleasing.
Did you know? Andhra Pradesh fashion is heavily influenced by its temple culture, with traditional attire often featuring temple jewelry and designs inspired by religious architecture, complemented by the practical clothing needs of its agricultural communities.
Traditional Andhra Pradesh men's attire reflects the state's rural heritage combined with cultural sophistication. From formal occasions to everyday wear, these garments showcase a unique cultural identity that has evolved over centuries.
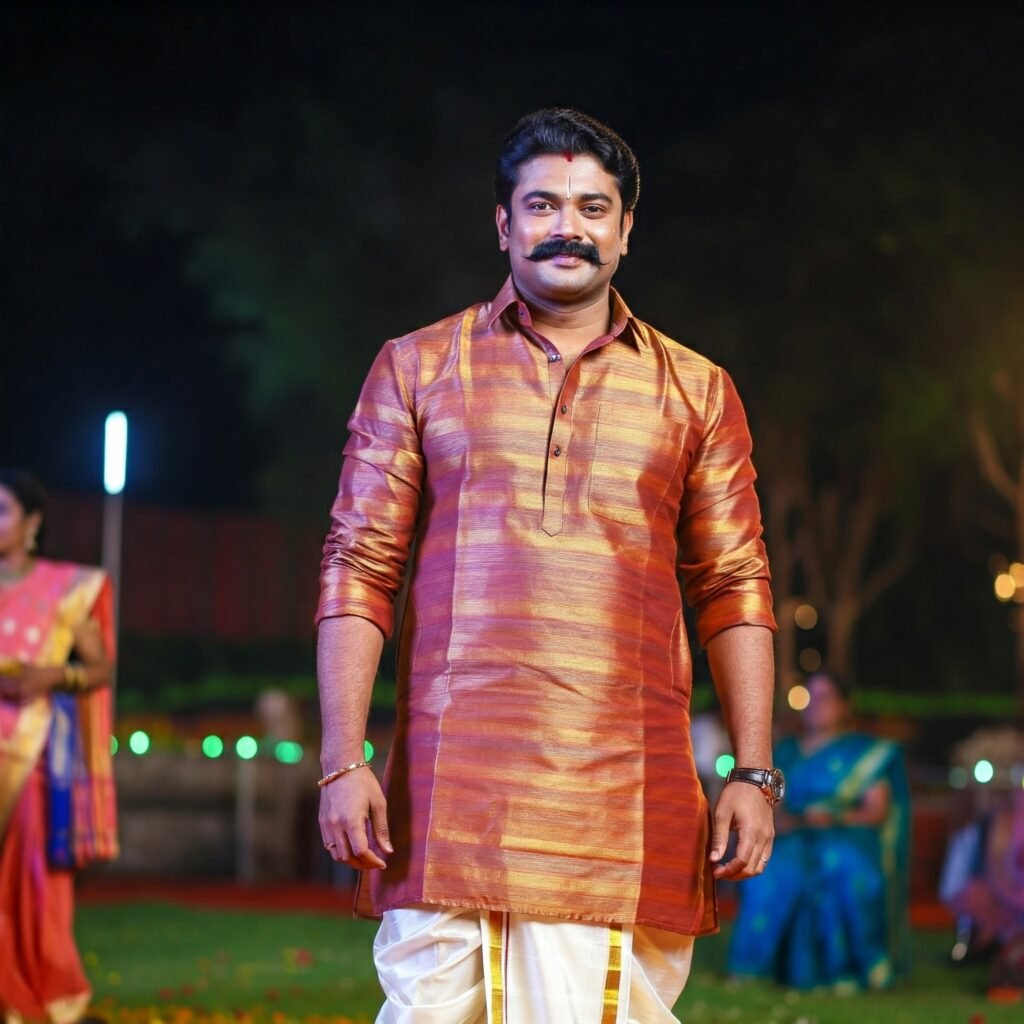

Traditional Andhra Pradesh men's fashion represents the harmonious blend of rural and urban influences. The retention of traditional elements while adapting to modern needs creates a unique sartorial identity that distinguishes Andhrites from other Indian communities.
Andhra Pradesh women's traditional attire is a beautiful representation of cultural elegance and practical needs. The clothing reflects both the aesthetic sensibilities of temple culture and the practical requirements of daily life in different regions of the state.
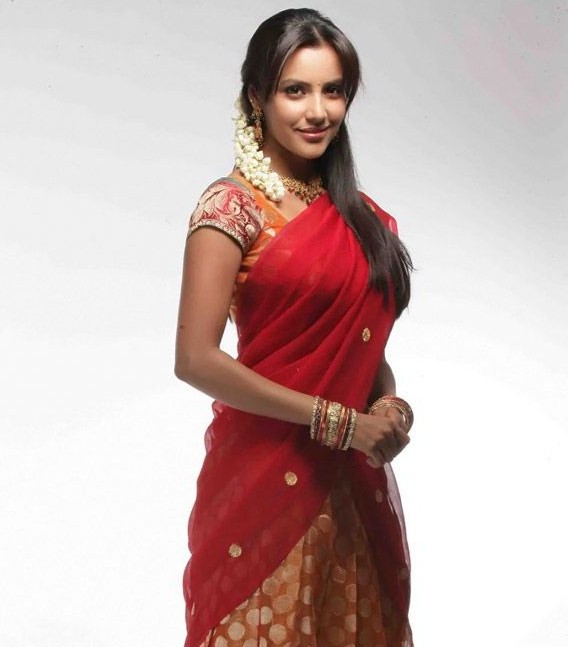


Women's fashion in Andhra Pradesh tells a story of cultural preservation and adaptation. The distinct styles between different regions showcase how local traditions were maintained while incorporating practical needs. The elegance of traditional attire reflects Andhra's temple culture, while the practical elements acknowledge the agricultural lifestyle of many communities.
Andhra Pradesh textiles reflect the state's agricultural heritage, cultural diversity, and historical trade connections. The fabrics used in traditional clothing prioritize comfort, breathability, and suitability for the region's climate.
The textile traditions of Andhra Pradesh have evolved significantly over centuries. Ancient textiles were primarily simple cottons with minimal decoration. During various dynastic rules, luxurious fabrics and techniques were introduced, leading to distinctive styles. In modern times, there has been a revival of traditional techniques alongside increased experimentation with contemporary materials.
Contemporary Andhra Pradesh fashion represents a dynamic blend of traditional elements with global influences, heavily shaped by urbanization, education, and the state's cosmopolitan culture. The modern Andhra wardrobe seamlessly transitions from traditional attire for festivals to contemporary styles for daily wear.
Traditional Telugu clothing dominated, with simple cotton garments suited for the agricultural lifestyle.
Temple influences introduced more elaborate designs, jewelry, and luxurious fabrics.
Post-independence period saw a blend of traditional Andhra and Western fashions.
Globalization and education accelerate fashion evolution, with Andhra designers creating fusion styles.
Andhra Pradesh has produced several fashion designers who have gained recognition for their work that often incorporates Andhra cultural elements.
Andhra Pradesh fashion is a dynamic and evolving expression of the state's unique cultural identity. Rooted in practical considerations for agricultural life and shaped by temple traditions, it represents a harmonious blend of simplicity and elegance. From the traditional sarees of rural women to the sophisticated silk dhotis of men, Andhra clothing tells a story of cultural continuity, adaptation, and pride in heritage.
As Andhra Pradesh continues to navigate the intersection of tradition and modernity, its fashion scene remains a vibrant reflection of this balance. The growing recognition of Andhra designers suggests an exciting future where traditional elements will continue to influence broader fashion trends while adapting to contemporary sensibilities.
Future Trends: The next decade will likely see increased emphasis on sustainable practices, technological integration in textile production, and further innovation in fusion wear that respects traditional craftsmanship while embracing global fashion currents.